“Know your disease and live pain free”
Rheumatoid Arthritis - English
Q. What is Rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease like diabetes, hypothyroidism etc. affecting mainly the joints in our body. The immune system which is supposed to protect us, starts attacking one’s own joints.Q. What is the cause for Rheumatoid arthritis?
The reason for its occurrence is genetic predisposition with various environmental factors (eg: Smoking, Bacterial & Viral infections etc.) precipitating it.Q. What are the symptoms?
Patients usually complain of multiple joint pains with or without swelling (predominantly small joints of hands) and typically morning stiffness of atleast ½ hour duration.Q. Who are affected?
Females in their 3rd and 4th decade are more affected. It can also affect men and children. Children in particular have to be treated properly as it can affect their growth status.Q. How to diagnose?
To consult your doctor and get few blood investigations (ESR, CRP, Rheumatoid factor, Anti CCP) done before starting treatment.Q. Is it limited only to joints?
No. Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic problem and can involve other organs like eyes, lungs, blood vessels, nerves, bones(osteoporosis) etc.Q. Why it should be diagnosed early?
If diagnosed early and started on treatment it becomes easier to control the disease with fewer drugs in lesser dosages. The joints won’t be destroyed and involvement of other organs can be prevented.Q. How are they treated?
Initially steroids, pain killers are given along with rheumatoid arthritis specific drugs like methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, sulfasalazine etc.Q. What about side effects?
If periodical (once in 2 to 3 months) blood tests (Blood counts, Liver function etc.) are done then no need to worry about side effects.Q. Any supportive measures along with drugs?
Physiotherapy like joint mobilisation and strengthening exercises are must along with drugs. Patient education is most important in managing this disease. Patient should be counselled regarding the time taken for action of these drugs(takes 2-3 months and not immediate), chances of joint pain worsening with seasonal changes or infections like viral fever, diarrhoea etc. No dietary restrictions are needed. Patient should always discuss with their doctors regarding any doubts in treatment and not stop drugs on their own.Q. Any newer treatment options available?
If the disease is not controlled with traditional drugs, now we have newer injections called BIOLOGICALS (eg: Golimumab, Etanercept, Rituximab, Tocilizumab etc.). These drugs help in controlling even severe disease and hence patients will be relieved of their joint pains. So early diagnosis and early initiation of treatment helps out patients in being pain free with no long term complications.Q. How to identify Rheumatoid arthritis early?
Presence of pain and stiffness in small joints of hand or feet for at least 30 minutes duration, on getting up from bed. Pain/stiffness reduces as we start moving around. Next stage, we notice pain and swelling of small and large joints of hands and legs.Q. Who are at risk for Rheumatoid arthritis? Can young people get Rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is more common in females between 30-50 years age group. It can involve males, elderly and even kids (Juvenile idiopathic arthritis)Q. What are the tests to be done to confirm Rheumatoid arthritis? Are they always positive?
- Rheumatoid factor and Anti CCP are positive in only 65-70% and in remaining it can be negative but still patient can have rheumatoid arthritis.
- ESR, CRP are tests which help in assessing the disease activity and usually they are elevated.
Q. Are steroids and pain killers the only treatment?
Definitely not. Steroids and pain killers are only given temporarily to reduce the pain and inflammation. The disease specific drugs take 8-12 weeks to start acting. Hence, steroids or pain killers are prescribed initially and then stopped.Q. What are the life style changes needed to manage Rheumatoid arthritis?
- Adequate sleep
- Exercises and Yoga/Meditation
- Healthy and balanced diet; Reduce carbohydrates and sugars; Fish intake (omega-3 fatty acid) might help.
Q. Is Rheumatoid arthritis curable? Or one has to suffer throughout his life?
Early initiation (less than 3 months) of treatment helps to control the disease better. Among 10 patients, 1 or 2 might be able to stop the drug on early and prompt initiation of RA specific drugs. Can be pain free without the help of pain killers or steroids and have a good quality of life.Q. What might happen if we don’t get treated for Rheumatoid arthritis?
Inadequate disease control leads to two issues:- Joint deformities
- Extra articular complications – involvement of other organs like lung, eyes, blood vessels etc.
Q. Whom to approach to get treated for Rheumatoid arthritis?
The specialist trained to treat autoimmune disease like rheumatoid arthritis is known as ‘Rheumatologist’.Q.. Who is a Rheumatologist? What are all the diseases treated by them?
Rheumatologist is a physician who after their training in internal medicine (MD), get trained in ‘Rheumatology’ during their specialization (DM). Rheumatologist manages all bone, joints and connective tissue disorders medically. eg: rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, lupus, Sjogren’s syndrome, systemic sclerosis, vasculitis, gout, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis etc.
Rheumatoid Arthritis - Tamil
Q. முடக்கு வாதம் என்றால் என்ன?
முடக்கு வாதம் (RA) என்பது ஒரு தன்னுடல் தாக்க நோயாகும், இதில் நமது சொந்த நோயெதிர்ப்பு அமைப்பு நமது உடல் பாகங்களை பாதிக்கிறது. ஆரம்பத்தில், இது முக்கியமாக மூட்டுகளை பாதிக்கிறது. நோய் சரியாகக் கட்டுப்படுத்தப்படாவிட்டால் மற்ற உறுப்புகளையும் பாதிக்கும்.Q. முடக்கு வாதத்தை ஆரம்பத்திலேயே கண்டறிவது எப்படி?
படுக்கையில் இருந்து எழுந்தவுடன் குறைந்தது 30 நிமிடங்களுக்கு கை அல்லது கால்களின் சிறிய மூட்டுகளில் வலி மற்றும் விறைப்பு இருப்பது. நாம் நகரத் தொடங்கும் போது வலி/விறைப்பு மெதுவாக குறையும். அடுத்த கட்டத்தில், கைகள் மற்றும் கால்களின் சிறிய மற்றும் பெரிய மூட்டுகளில் வலி மற்றும் வீக்கத்தை நாம் கவனிக்கிறோம்.Q. முடக்கு வாதத்திற்கு யார் ஆபத்தில் உள்ளனர்? இளைஞர்களுக்கு முடக்கு வாதம் வருமா?
30-50 வயதுக்குட்பட்ட பெண்களில் முடக்கு வாதம் அதிகம் காணப்படுகிறது. இது ஆண்கள், வயதானவர்கள் மற்றும் குழந்தைகளை உள்ளடக்கியது (இளைஞர் இடியோபாடிக் ஆர்த்ரிடிஸ்).Q. முடக்கு வாதத்தை உறுதிப்படுத்த என்னென்ன சோதனைகள் செய்ய வேண்டும்? அவை எப்போதும் நேர்மறையானதா?
- முடக்கு காரணி மற்றும் எதிர்ப்பு CCP ஆகியவை 65-70% மட்டுமே நேர்மறையானவை, மீதமுள்ளவை எதிர்மறையாக இருக்கலாம், ஆனால் இன்னும் நோயாளிக்கு முடக்கு வாதம் இருக்கலாம்.
- ESR, CRP ஆகியவை நோயின் செயல்பாட்டை மதிப்பிடுவதற்கு உதவும் சோதனைகள் மற்றும் பொதுவாக அவை உயர்த்தப்படுகின்றன.
Q. ஸ்டெராய்டுகள் மற்றும் வலி நிவாரணிகள் மட்டுமே சிகிச்சையா?
நிச்சயமாக இல்லை. வலி மற்றும் வீக்கத்தைக் குறைக்க ஸ்டீராய்டுகள் மற்றும் வலி நிவாரணிகள் தற்காலிகமாக மட்டுமே கொடுக்கப்படுகின்றன. நோய் குறிப்பிட்ட மருந்துகள் செயல்படத் தொடங்க 8-12 வாரங்கள் ஆகும். எனவே, ஸ்டெராய்டுகள் அல்லது வலி நிவாரணிகள் ஆரம்பத்தில் பரிந்துரைக்கப்பட்டு பின்னர் நிறுத்தப்படுகின்றன.Q. முடக்கு வாதத்திற்கான தற்போதைய சிகிச்சை விருப்பங்கள் என்ன?
முடக்கு வாதத்திற்கு இரண்டு செட் மருந்துகள் உள்ளன: வழக்கமான மருந்துகள் மற்றும் புதிய மருந்துகள். இந்த மருந்துகள் நோயை மாற்றியமைக்கின்றன. இவை வலி நிவாரணிகள் அல்ல.வழக்கமான மருந்துகள்: மெத்தோட்ரெக்ஸேட் (Methotrexate), சல்பசலாசின்(Sulfasalazine), ஹைட்ராக்ஸி குளோரோகுயின் (Hydroxychloroquine), லெஃப்ளூனோமைடு (Leflunomide), இகுராடிமோட் (Iguratimod)
சிறிய மூலக்கூறுகள்/JAK தடுப்பான்கள்: Tofacitinib, Baricitinib உயிரியியல் (Biologics): Etanercept, Infliximab, Adalimumab, Golimumab, Rituximab, Tocilizumab.
Q. முடக்கு வாதத்தை நிர்வகிக்க என்ன வாழ்க்கை முறை மாற்றங்கள் தேவை?
- போதுமான தூக்கம்
- உடற்பயிற்சிகள் மற்றும் யோகா/தியானம்
- ஆரோக்கியமான மற்றும் சீரான உணவு; கார்போஹைட்ரேட்டுகள் மற்றும் சர்க்கரைகளைக் குறைக்கவும்; மீன் உட்கொள்ளல் (ஒமேகா -3 கொழுப்பு அமிலம்) உதவக்கூடும்.
Q. முடக்கு வாதம் குணமாகுமா? அல்லது ஒருவன் தன் வாழ்நாள் முழுவதும் கஷ்டப்பட வேண்டுமா?
ஆரம்பகால சிகிச்சை (3 மாதங்களுக்கும் குறைவானது) நோயை சிறப்பாகக் கட்டுப்படுத்த உதவுகிறது. 10 நோயாளிகளில், 1 அல்லது 2 பேர் RA குறிப்பிட்ட மருந்துகளின் ஆரம்ப மற்றும் உடனடி துவக்கத்தில் மருந்தை நிறுத்த முடியும். வலி நிவாரணிகள் அல்லது ஸ்டெராய்டுகளின் உதவியின்றி வலி இல்லாமல் இருக்க முடியும் மற்றும் நல்ல வாழ்க்கைத் தரத்தைப் பெறலாம்.Q. முடக்கு வாதத்திற்கு நாம் சிகிச்சை பெறாவிட்டால் என்ன நடக்கும்?
போதுமான நோய் கட்டுப்பாடு இரண்டு சிக்கல்களுக்கு வழிவகுக்கிறது:- கூட்டு சிதைவுகள்
- கூடுதல் மூட்டு சிக்கல்கள் - நுரையீரல், கண்கள், இரத்த நாளங்கள் போன்ற பிற உறுப்புகளின் ஈடுபாடு.
Q. முடக்கு வாதத்திற்கு சிகிச்சை பெற யாரை அணுக வேண்டும்?
முடக்கு வாதம் போன்ற ஆட்டோ இம்யூன் நோய்க்கு சிகிச்சையளிப்பதற்கு பயிற்சி பெற்ற நிபுணர் 'ருமாட்டாலஜிஸ்ட்' என்று அழைக்கப்படுகிறார்.Q. வாத நோய் நிபுணர் யார்? அவர்களால் எந்த நோய்களுக்கு சிகிச்சை அளிக்கப்படுகிறது?
ருமாட்டாலஜிஸ்ட் ஒரு மருத்துவர் ஆவார், அவர் உள் மருத்துவத்தில் (MD) பயிற்சி பெற்ற பிறகு, அவர்களின் நிபுணத்துவத்தின் போது (DM) ‘ருமாட்டாலஜி’யில் பயிற்சி பெறுகிறார்.அனைத்து எலும்புகள், மூட்டுகள் மற்றும் இணைப்பு திசு கோளாறுகளை மருத்துவ ரீதியாக வாத மருத்துவர் நிர்வகிக்கிறார்.
எ.கா: முடக்கு வாதம், அன்கிலோசிங் ஸ்பான்டைலிடிஸ், சொரியாடிக் ஆர்த்ரிடிஸ், லூபஸ், ஸ்ஜோகிரென்ஸ் சிண்ட்ரோம், சிஸ்டமிக் ஸ்களீரோசிஸ், வாஸ்குலிடிஸ், கீல்வாதம், ஆஸ்டியோபோரோசிஸ், கீல்வாதம் போன்றவை.
Sjogrens Syndrome - English
Q. What is Sjogrens syndrome?
Sjogren s syndrome is an autoimmune disease where our own immune system affects our salivary and lacrimal glands and can cause dryness of mouth and eyes. It can also cause fatigue, joint pains and can affect the internal organs.Q. How to identify Sjogrens syndrome early?
Dry eyes and/or dry mouth lasting for more than 3 months, tiredness and musculoskeletal pain are the common early symptoms. The following are the other symptoms that can occur in patients with Sjogrens syndrome:- Neurological problems
- Swollen salivary glands
- Difficulty swallowing, heartburn
- Skin rashes
- Lung, liver and renal problems
- Skin and vaginal dryness
Q. Who are at risk for Sjogrens?
Most patients with Sjogrens syndrome are women between 40- 60 years. However, it can affect men and people of all age groups including children.Q. How is Sjogrens diagnosed?
The diagnosis is based on the clinical manifestations, blood tests (70% of Sjögren’s patients are positive for SS-A and 40% are positive for SS-B antibodies), eye tests to measure tear production (Schirmer test) and biopsy of the salivary glands (usually in lower lip)/nerves/ skin may also be required.Q. Which doctor should I consult?
Rheumatologists are often the primary doctors treating Sjogrens. However, ophthalmologists, dentists and other specialists may be involved depending on the organ involved.Q. What medications will I require?
Symptomatic treatment may be required if dryness is troublesome. Immunomodulators or immunosuppressants may also be required depending upon the manifestations.Q. Is it OK to take immunosuppressants?
Immunosupressants are only prescribed when their benefits outweigh the harm and they help control the disease and prevent organ damage.Q. How long will I require treatment?
Sjogrens disease is a chronic disease like diabetes and hypertension requiring medications for a long time. However, some patients may be able to come off medications later.Q. What happens if I don’t get treated?
Failure to get treated may result in permanent organ damage which can be prevented with early treatment. Treatment also greatly improves the quality of life.Q. Can I become pregnant when having Sjogrens?
Sjogrens usually does not affect the ability to conceive. It is important that you consult your rheumatologist prior to planning pregnancy.Q. Can Sjogrens affect my child?
Presence of anti-RO antibodies in the mother can cause congenital heart block in about 1 in 100 pregnancies and repeated fetal echoes are required during pregnancy. There are medications which can reduce this risk but not completely mitigate it. Neonatal lupus is another condition which can affect the baby but it is usually transient.Q. What lifestyle changes do I need to adopt?
Adequate sleep, regular exercise, healthy diet and a positive mindset go a long way in managing Sjogrens.
Sjogrens Syndrome - Tamil
Q. ஸ்ஜோக்ரென்ஸ் நோய்க்குறி என்றால் என்ன?
Sjogren s சிண்ட்ரோம் என்பது ஒரு தன்னுடல் தாக்க நோயாகும், இதில் நமது சொந்த நோயெதிர்ப்பு அமைப்பு நமது உமிழ்நீர் மற்றும் கண்ணீர் சுரப்பிகளை பாதிக்கிறது மற்றும் வாய் மற்றும் கண்களின் வறட்சியை ஏற்படுத்தும். இது சோர்வு, மூட்டு வலி மற்றும் உள் உறுப்புகளை பாதிக்கும்.Q. ஸ்ஜோக்ரென்ஸ் நோய்க்குறியை ஆரம்பத்திலேயே கண்டறிவது எப்படி?
வறண்ட கண்கள் மற்றும்/அல்லது 3 மாதங்களுக்கும் மேலாக நீடிக்கும் வாய் வறட்சி, சோர்வு மற்றும் தசைக்கூட்டு வலி ஆகியவை பொதுவான ஆரம்ப அறிகுறிகளாகும்.ஸ்ஜோக்ரென்ஸ் நோய்க்குறி நோயாளிகளுக்கு ஏற்படக்கூடிய பிற அறிகுறிகள் பின்வருமாறு:
- நரம்பியல் பிரச்சனைகள்
- வீங்கிய உமிழ்நீர் சுரப்பிகள்
- விழுங்குவதில் சிரமம், நெஞ்செரிச்சல்
- தோல் வெடிப்புகள்
- நுரையீரல், கல்லீரல் மற்றும் சிறுநீரக பிரச்சனைகள்
- தோல் மற்றும் பிறப்புறுப்பு வறட்சி
Q. ஸ்ஜோக்ரென்ஸுக்கு யார் ஆபத்தில் உள்ளனர்?
ஸ்ஜோக்ரென்ஸ் நோய்க்குறி உள்ள பெரும்பாலான நோயாளிகள் 40-60 வயதுக்குட்பட்ட பெண்கள். இருப்பினும், இது ஆண்கள் மற்றும் குழந்தைகள் உட்பட அனைத்து வயதினரையும் பாதிக்கலாம்.Q. Sjogrens எவ்வாறு கண்டறியப்படுகிறது?
நோயறிதல் மருத்துவ வெளிப்பாடுகள், இரத்த பரிசோதனைகள் (70% Sjögren நோயாளிகள் SS-A க்கு நேர்மறையாகவும், 40% SS-B ஆன்டிபாடிகளுக்கு நேர்மறையாகவும் உள்ளனர்), கண்ணீர் உற்பத்தியை அளவிடுவதற்கான கண் சோதனைகள் (Schirmer சோதனை) மற்றும் உமிழ்நீரின் பயாப்ஸி ஆகியவற்றை அடிப்படையாகக் கொண்டது. சுரப்பிகள் (பொதுவாக கீழ் உதட்டில்)/நரம்புகள்/தோல் தேவைப்படலாம்.Q. நான் எந்த மருத்துவரை அணுக வேண்டும்?
வாதநோய் நிபுணர்கள் பெரும்பாலும் ஸ்ஜோகிரென்ஸுக்கு சிகிச்சை அளிக்கும் முதன்மை மருத்துவர்கள். இருப்பினும், சம்பந்தப்பட்ட உறுப்பைப் பொறுத்து கண் மருத்துவர்கள், பல் மருத்துவர்கள் மற்றும் பிற நிபுணர்கள் ஈடுபடலாம்.Q. எனக்கு என்ன மருந்துகள் தேவைப்படும்?
வறட்சி தொந்தரவாக இருந்தால் அறிகுறி சிகிச்சை தேவைப்படலாம். வெளிப்பாடுகளைப் பொறுத்து இம்யூனோமோடூலேட்டர்கள் அல்லது நோயெதிர்ப்புத் தடுப்பு மருந்துகள் தேவைப்படலாம்.Q. நோய்த்தடுப்பு மருந்துகளை எடுத்துக்கொள்வது சரியா?
நோயெதிர்ப்புத் தடுப்பு மருந்துகள் அவற்றின் நன்மை தீமையை விட அதிகமாக இருக்கும்போது மட்டுமே பரிந்துரைக்கப்படுகின்றன, மேலும் அவை நோயைக் கட்டுப்படுத்தவும் உறுப்பு சேதத்தைத் தடுக்கவும் உதவுகின்றன.Q. எனக்கு எவ்வளவு காலம் சிகிச்சை தேவைப்படும்?
ஸ்ஜோக்ரென்ஸ் நோய் என்பது நீரிழிவு மற்றும் உயர் இரத்த அழுத்தம் போன்ற ஒரு நாள்பட்ட நோயாகும், இது நீண்ட காலத்திற்கு மருந்துகள் தேவைப்படும். இருப்பினும், சில நோயாளிகள் பின்னர் மருந்துகளை விட்டு வெளியேறலாம்.Q. நான் சிகிச்சை பெறாவிட்டால் என்ன நடக்கும்?
சிகிச்சை பெறத் தவறினால் நிரந்தர உறுப்பு சேதம் ஏற்படலாம், இது ஆரம்ப சிகிச்சை மூலம் தடுக்கப்படலாம். சிகிச்சையானது வாழ்க்கைத் தரத்தையும் பெரிதும் மேம்படுத்துகிறது.Q. ஸ்ஜோக்ரென்ஸ் இருக்கும்போது நான் கர்ப்பமாக முடியுமா?
Sjogrens பொதுவாக கருத்தரிக்கும் திறனை பாதிக்காது. கர்ப்பத்தைத் திட்டமிடுவதற்கு முன், உங்கள் வாத மருத்துவரிடம் ஆலோசனை பெறுவது முக்கியம்.Q. Sjogrens என் குழந்தையை பாதிக்குமா?
தாய்க்கு RO எதிர்ப்பு ஆன்டிபாடிகள் இருப்பதால், 100 கர்ப்பங்களில் 1ல் பிறவி இதய அடைப்பு ஏற்படலாம் மற்றும் கர்ப்ப காலத்தில் மீண்டும் மீண்டும் கரு எதிரொலி தேவைப்படுகிறது. இந்த ஆபத்தை குறைக்கக்கூடிய மருந்துகள் உள்ளன, ஆனால் அதை முழுமையாக குறைக்க முடியாது. நியோனாடல் லூபஸ் என்பது குழந்தையை பாதிக்கும் மற்றொரு நிலை, ஆனால் இது பொதுவாக நிலையற்றது.Q. என்ன வாழ்க்கைமுறை மாற்றங்களை நான் பின்பற்ற வேண்டும்?
போதுமான தூக்கம், வழக்கமான உடற்பயிற்சி, ஆரோக்கியமான உணவு மற்றும் நேர்மறையான மனநிலை ஆகியவை Sjogrens ஐ நிர்வகிப்பதில் நீண்ட தூரம் செல்கின்றன.
Systemic Sclerosis - English
Q. What is systemic sclerosis?
Systemic sclerosis is an autoimmune disease that affects skin and many internal organs. Also called scleroderma, means hardening of skin.Q. What are the types of scleroderma?
Scleroderma can be classified as localized (where only some part of the skin is involved) or systemic (skin and internal organs are involved). Systemic sclerosis is of two types, limited cutaneous and diffuse cutaneous.Q. Who are the people affected by systemic sclerosis?
Systemic sclerosis mostly affects women between 30-50 years of age. Rarely it can affect children, where it is called as juvenile scleroderma.Q. What causes systemic sclerosis?
Interaction between genetic factors and environmental triggers like exposure to insecticides, viruses, some drugs lead to autoimmunity which causes systemic sclerosis.Q. What are the symptoms of systemic sclerosis?
Patient can have cold sensation of fingertips and toes with colour change which can get aggravated by keeping hands in cold water (Raynaud’s phenomenon). They can have ulcers over fingertips and hardening of the skin over hands, legs and face. Patient can have difficulty in swallowing, difficulty in breathing, chest pain, dry cough, abdominal bloating, constipation, weight loss and joint pain due to internal organ involvement.Q. How do we diagnose systemic sclerosis?
Systemic sclerosis can be diagnosed by clinical examination and by doing some laboratory investigations.Q. How do we treat patients with systemic sclerosis?
Systemic sclerosis patients are treated with antiraynauds medicines like calcium channel blockers, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, and ACE inhibitors. Drugs like Proton pump inhibitors and prokinetic agents to prevent gastric symptoms. Immunosuppressive medicines like mycophenolate mofetil, cyclophosphamide and rituximab may be needed in severe cases.Q. What are the general precautions to be followed by a systemic sclerosis patient?
Avoid exposure to cold water, cold temperature by using wollen gloves and socks and by keeping hands and feets in warm water. Avoid smoking. To take small, frequent, less spicy foods. To avoid lying down immediately after taking foods. To sleep with head end elevation. To keep the skin moisturized. To do regular physical exercises to keep joints active.Q. What are the complications of systemic sclerosis?
Systemic sclerosis can affect internal organs like lungs, heart, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract which lead to complications like interstitial lung disease, pulmonary hypertension, respiratory failure, heart blocks, renal failure, bleeding from gut, bowel obstruction, skin ulcers and gangrene.Q. How does systemic sclerosis affect pregnancy?
If patient has severe lung disease or heart disease like pulmonary artery hypertension, then pregnancy carries high risk, hence not advised. Pregnancy can be planned, in case of mild and well controlled disease without major internal organ involvement, as per the doctor’s advice.
Systemic Sclerosis - Tamil
Q. சிஸ்டமிக் ஸ்களீரோசிஸ் என்றால் என்ன?
சிஸ்டமிக் ஸ்களீரோசிஸ் என்பது ஒரு தன்னுடல் தாக்க நோயாகும், இது தோல் மற்றும் பல உள் உறுப்புகளை பாதிக்கிறது. ஸ்க்லெரோடெர்மா என்றும் அழைக்கப்படுகிறது, அதாவது தோலை கடினப்படுத்துகிறது.Q. ஸ்க்லரோடெர்மாவின் வகைகள் என்ன?
ஸ்க்லெரோடெர்மாவை குறிப்பிட்ட இடத்தில் (தோலின் ஒரு பகுதி மட்டுமே சம்பந்தப்பட்டது) அல்லது அமைப்பு (தோல் மற்றும் உள் உறுப்புகளை பாதிக்கும்) என வகைப்படுத்தலாம். சிஸ்டமிக் ஸ்களீரோசிஸ் என்பது வரையறுக்கப்பட்ட வகை மற்றும் பரவலான வகை என இரண்டு வகைகளாகும்.Q. சிஸ்டமிக் ஸ்களீரோசிஸ் யாருக்கு வரும்?
சிஸ்டமிக் ஸ்களீரோசிஸ் பெரும்பாலும் 30-50 வயதுடைய பெண்களை பாதிக்கிறது. அரிதாக இது குழந்தைகளை பாதிக்கலாம், அங்கு இது இளம் ஸ்க்லரோடெர்மா என்று அழைக்கப்படுகிறது.Q. சிஸ்டமிக் ஸ்களீரோசிஸ் எதனால் ஏற்படுகிறது?
மரபணு காரணிகள் மற்றும் பூச்சிக்கொல்லிகள், வைரஸ்கள் மற்றும் மருந்துகளின் வெளிப்பாடு போன்ற சுற்றுச்சூழல் தூண்டுதல்களுக்கு இடையிலான தொடர்பு தன்னுடல் எதிர்ப்பு சக்திக்கு வழிவகுக்கிறது, இது ஸ்க்லரோடெர்மாவை ஏற்படுத்துகிறது.Q. சிஸ்டமிக் ஸ்களீரோசிஸின் அறிகுறிகள் என்ன?
குளிர்ந்த நீரில் கைகளை வைத்திருப்பதன் மூலம் நோயாளியின் நிற மாற்றத்துடன் விரல் நுனிகள் மற்றும் கால்விரல்களில் குளிர்ச்சியான உணர்வு ஏற்படலாம் (ரேனாட் நிகழ்வு). அவர்கள் விரல் நுனியில் புண்கள் மற்றும் கைகள், கால்கள் மற்றும் முகம் மீது தோல் கடினப்படுத்தலாம். உள் உறுப்புகளின் ஈடுபாட்டினால் நோயாளிக்கு விழுங்குவதில் சிரமம், சுவாசிப்பதில் சிரமம், மார்பு வலி, வறட்டு இருமல், வயிற்று உப்புசம், மலச்சிக்கல், எடை இழப்பு மற்றும் மூட்டு வலி போன்றவை ஏற்படலாம்.Q. சிஸ்டமிக் ஸ்களீரோசிஸை எவ்வாறு கண்டறிவது?
சிஸ்டமிக் ஸ்களீரோசிஸ் மருத்துவ பரிசோதனை மற்றும் சில ஆய்வக ஆய்வுகள் மூலம் கண்டறிய முடியும்.Q. சிஸ்டமிக் ஸ்களீரோசிஸுக்கு என்ன சிகிச்சை அளிக்கப்படுகிறது?
சிஸ்டமிக் ஸ்களீரோசிஸ் நோயாளிகளுக்கு கால்சியம் சேனல் தடுப்பான்கள், பாஸ்போடிஸ்டேரேஸ் தடுப்பான்கள் மற்றும் ஏசிஇ தடுப்பான்கள் போன்ற ஆன்டிராய்னாட்ஸ் மருந்துகளுடன் சிகிச்சை அளிக்கப்படுகிறது. இரைப்பை அறிகுறிகளைத் தடுக்க புரோட்டான் பம்ப் இன்ஹிபிட்டர்கள் மற்றும் புரோகினெடிக்ஸ் போன்ற மருந்துகள் பயன்படுத்தப்படுகின்றன. மைக்கோபெனோலேட் மொஃபெடில், சைக்ளோபாஸ்பாமைடு மற்றும் ரிட்டுக்சிமாப் போன்ற நோயெதிர்ப்புத் தடுப்பு மருந்துகள் கடுமையான சந்தர்ப்பங்களில் தேவைப்படலாம்.Q. சிஸ்டமிக் ஸ்களீரோசிஸ் நோயாளி பின்பற்ற வேண்டிய பொதுவான முன்னெச்சரிக்கைகள் என்ன?
குளிர்ந்த நீர், குளிர் வெப்பநிலை வெளிப்படுவதை தவிர்க்கவும். கம்பளி கையுறைகள் மற்றும் காலுறைகளைப் பயன்படுத்தவும், கைகளையும் கால்களையும் வெதுவெதுப்பான நீரில் வைக்கவும். புகைபிடிப்பதைத் தவிர்க்க. சிறிய, அடிக்கடி, குறைந்த காரமான உணவுகளை எடுத்துக்கொள்ள வேண்டும். உணவு உட்கொண்ட உடனேயே படுத்துக் கொள்வதைத் தவிர்க்க வேண்டும். தலையை உயர்த்தி தூங்க வேண்டும். சருமத்தை ஈரப்பதத்துடன் வைத்திருக்க. மூட்டுகளை சுறுசுறுப்பாக வைத்திருக்க வழக்கமான உடற்பயிற்சிகளை செய்ய வேண்டும்.Q. சிஸ்டமிக் ஸ்களீரோசிஸின் சிக்கல்கள் என்ன?
சிஸ்டமிக் ஸ்களீரோசிஸ் நுரையீரல், இதயம், சிறுநீரகம், இரைப்பை குடல் போன்ற உள் உறுப்புகளை பாதிக்கலாம், இது இடைநிலை நுரையீரல் நோய், நுரையீரல் உயர் இரத்த அழுத்தம், சுவாச செயலிழப்பு, இதய அடைப்புகள், சிறுநீரக செயலிழப்பு, குடலில் இருந்து இரத்தப்போக்கு, குடல் அடைப்பு, தோல் புண்கள் போன்ற சிக்கல்களுக்கு வழிவகுக்கும்.Q. சிஸ்டமிக் ஸ்களீரோசிஸ் கர்ப்பத்தை எவ்வாறு பாதிக்கிறது?
நோயாளிக்கு கடுமையான நுரையீரல் நோய் அல்லது நுரையீரல் தமனி உயர் இரத்த அழுத்தம் போன்ற இதய நோய் இருந்தால், கர்ப்பம் அதிக ஆபத்தைக் கொண்டுள்ளது, எனவே பரிந்துரைக்கப்படவில்லை. மருத்துவரின் ஆலோசனையின்படி, பெரிய உள் உறுப்புகள் சம்பந்தப்படாமல், லேசான மற்றும் நன்கு கட்டுப்படுத்தப்பட்ட நோய் ஏற்பட்டால், கர்ப்பத்தைத் திட்டமிடலாம்.
Psoriatic Arthritis - English
Q. What is Psoriatic Arthritis?
Joint pains, spinal pains, entheseal pains (achilles tendinitis, plantar fasciitis, tennis elbow) and dactylitis(sausage like swelling of digits with redness and pain) in a patient with current or past Psoriasis or family history of Psoriasis is called as Psoriatic arthritis. The joints involved are hand joints, knee, shoulder, joints of the feet along with a special joint in the lower back called as sacro-iliac joint.Q. Is Psoriatic arthritis different from Rheumatoid Arthritis?
It is different from Rheumatoid Arthritis(RA). Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) affects males and females equally, affect spine more, enthesitis incidence is more with PsA, will have negative rheumatoid factor and negative anti-CCP and it is highly deforming when compared to RA. If untreated or inadequately treated it may lead to irreversible deformities.Q. How does a rheumatologist diagnose a Psoriatic Arthritis?
A rheumatologist takes proper history, studies the pattern of the joints involved, does some basic blood investigation and if needed do an imaging (Xray MRI).Q. Is Psoriatic Arthritis a life-long disease?
Yes, it is; most chronic auto-immune diseases are life long disease. That’s the reason its all the more important to stick on to your rheumatologist for making your life easier. Leading a healthy, pain-free life with the support of a good life-style and necessary drugs would make life a breeze in such patients.Q. Is it Genetic? Does it spread?
Psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis can run in family; it can have genetic transmission. Close to 30% of individuals with Psoriatic arthritis can have one first degree relative with either Psoriasis or Psoriatic arthritis. But psoriasis or PsA is not communicable. It doesn’t spread between family members. Patients with PsA should not face any discrimination in any walks of life.Q. Rheumatologist role in treatment?
A rheumatologist after assessing selects the best DMARDs for PsA tailoring it according to the patient’s symptom. The dose is adjusted frequently since the stable dose needed to achieve disease remission differs between individuals. Side-effects of drugs would be monitored. If the patient does not respond to conventional treatment, advanced treatment like biologics would be started.Q. Can a person male/female on medications marry? Have kids?
A person with Psoriasis and Psoriatic arthritis can lead a normal life; get married and rear kids. A rheumatologist after assessing the disease state would change to treatment which can be safe for having kids. There are certain drugs used for treating PsA which are safe during pregnancy and lactation.Q. What are the other complications apart from deforming arthritis in PsA?
Psoriatic arthritis can lead to nail changes, nail dystrophy, metabolic syndrome, high uric acid, inflammatory bowel disease, increase the incidence of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Coronary artery disease and causes psychological impact. In short, it affects activities of daily living and leads to chronic illness. A single line of suggestion to patients with any chronic inflammatory joint disease is to connect to a rheumatologist today. Close to 50% of cases remain unrecognized in primary and secondary care settings and even a 6 month delay can lead on to deforming arthritis. So donot delay your visit to a rheumatologist.Patient Story
Mr.X a 28-year-old, software engineer had seen multiple doctors for his foot pain in the past 6 months. He had been treated with NSAIDs (Pain killers) and advised foot wear change. His uric acid was high at 8 mg/dL. He was treated with uric acid lowering drugs too. His condition did not improve by much. The pain was limiting his day-to-day activities and he seemed to be NSAID dependent. That’s when he visited a rheumatologist. A rheumatologist is a doctor who deals with inflammatory disorders of joints and essentially treat auto-immune disorder.
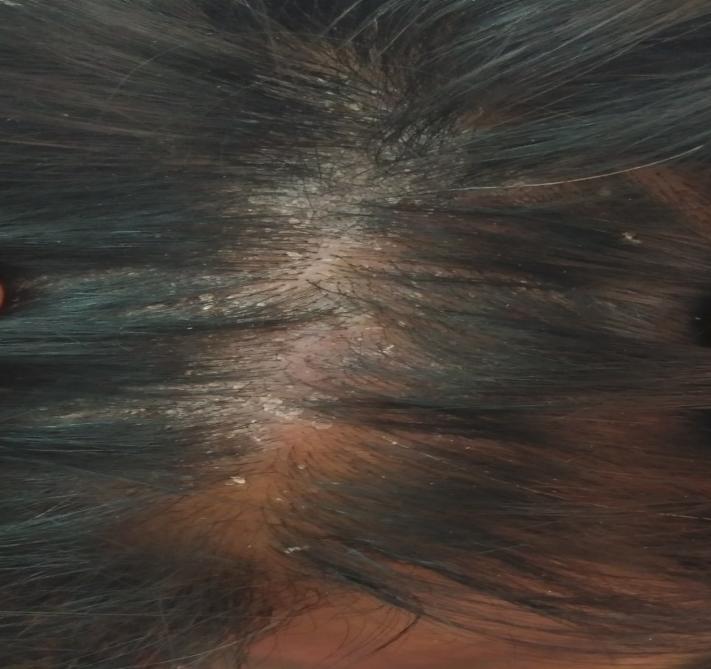
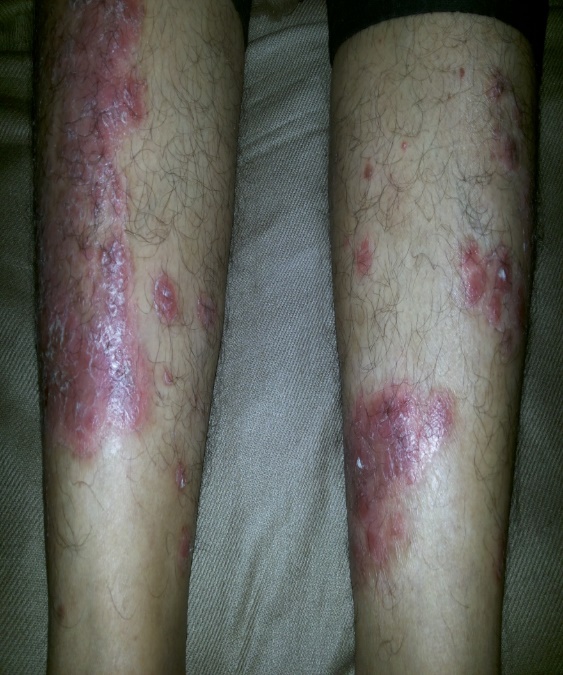
Having listened to his history the first question he was asked was, “Do you have Psoriasis?” Yes! was the answer. Went on to show the scalp psoriasis and scaly lesions in the hands and legs. Why didn’t he tell it to any doctors previously? He wasn’t asked, neither was he aware that there is a relation between skin and joints. With a diagnosis of Psoriatic arthritis made by the treating rheumatologist, he was started on Disease Modifying Anti Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs). He is currently pain free; not using any pain killers and on regular follow up. This case study re-emphasis the fact Rheumatologist are specialist doctors who could be of major help to patients suffering from inflammatory joint pathology.
Having listened to his history the first question he was asked was, “Do you have Psoriasis?” Yes! was the answer. Went on to show the scalp psoriasis and scaly lesions in the hands and legs. Why didn’t he tell it to any doctors previously? He wasn’t asked, neither was he aware that there is a relation between skin and joints. With a diagnosis of Psoriatic arthritis made by the treating rheumatologist, he was started on Disease Modifying Anti Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs). He is currently pain free; not using any pain killers and on regular follow up. This case study re-emphasis the fact Rheumatologist are specialist doctors who could be of major help to patients suffering from inflammatory joint pathology.
Psoriasis in scalp and over the legs in a Young Male